-
Hints of horizontal gene transfer
This example is a recreation of case study 2 (Figure 4) in the original publication of fusionDB here. Recoloring the visualization by temperature preference shows clear separation between mesophiles and thermophiles. Investigating the graph in interactive visualization mode we can observe that the three Bacilli organism that are thermophilic are functionally closer to the thermophilic Clostridia organisms then to other evolutionary closer related mesophilic Bacilli.
Organism Genus Temperature Preference Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DSM 7 Bacilli Mesophile Bacillus anthracis A0248 Bacilli Mesophile Bacillus cereus ATCC 14579 Bacilli Mesophile Bacillus coagulans 2 6 Bacilli Thermophile Bacillus coagulans 36D1 Bacilli Thermophile Bacillus licheniformis ATCC 14580 Bacilli Mesophile Bacillus megaterium DSM319 Bacilli Mesophile Bacillus subtilis 168 Bacilli Mesophile Bacillus thuringiensis Al Hakam Bacilli Mesophile Bacillus tusciae DSM 2912 Bacilli Thermophile Bacillus weihenstephanensis KBAB4 Bacilli Psychrotolerant Desulfotomaculum carboxydivorans CO 1 SRB Clostridia Thermophile Sulfobacillus acidophilus TPY Clostridia Thermophile 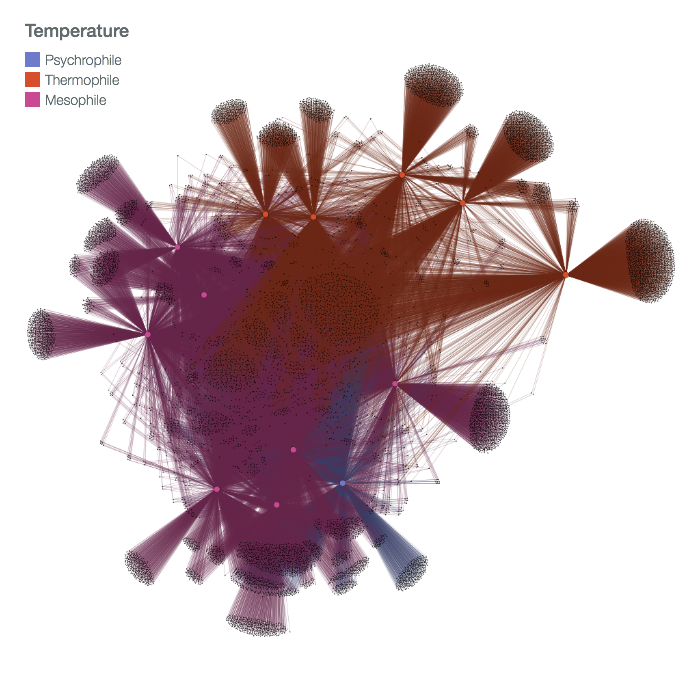
-
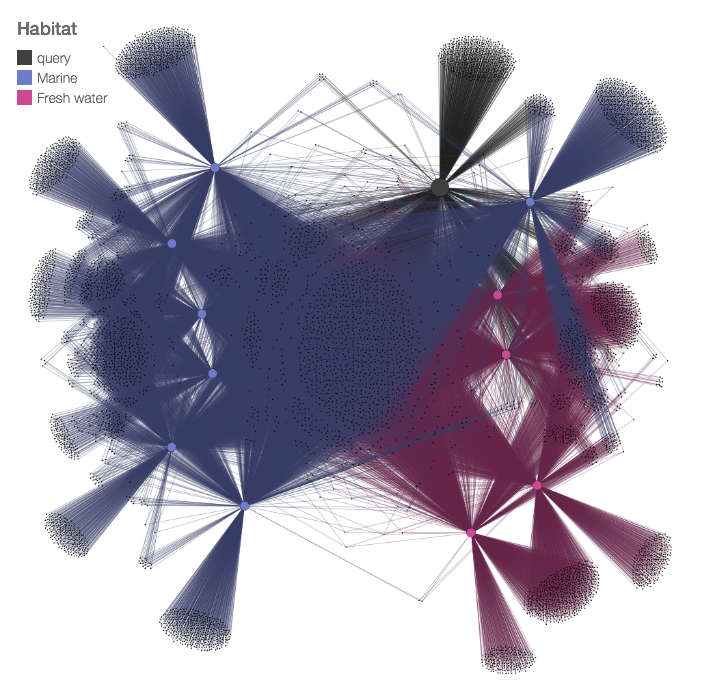
Mapping a previously unknown Synechococcus into fusionDB
In this example we chose to map a Synechococcus that is presently not in fusionDB. Coloring the fusion+ visualization by habitat preference a clear separation into marine and fresh water organisms is visible, with the exception of one organism. Using the interactive display we were able to extract exactly which organism this is (Synechococcus PCC 7002), with the information that this microbe was actually extracted from marine mud. Further investigation in available literature revealed that this organism despite being salt tolerant does not require salt to grow, and therefore possibly has a closer functional relatedness to fresh water organisms than marine organisms. Additionally the query organism (of which it is known that this Synechococcus is extracted from a fresh water enviroment) clusters well with other fresh water Synechococcus. Functional relatedness to other organisms and the functional repertoire this Synechococcus was mapped to can also be investigated here.
Organism Habitat Synechococcus PCC 7502 (Query) Fresh water Synechococcus PCC 7002 Marine (Mud) Synechococcus elongatus PCC 7942 Fresh water Synechococcus elongatus PCC 6301 Fresh water Synechococcus JA 2 3B a 2 13 Fresh water Synechococcus JA 3 3Ab Fresh water Synechococcus WH 8102 Marine Synechococcus CC9311 Marine Synechococcus RCC307 Marine Synechococcus WH 7803 Marine Synechococcus CC9605 Marine Synechococcus CC9902 Marine